[ad_1]

Two bills proposed in Illinois this year illustrate yet again the need for lawmakers to better understand how insurance works. Illinois HB 4767 and HB 4611 – like their 2023 predecessor, HB 2203 – would harm the very policyholders the measures aim to help by driving up the cost for insurers to write personal auto coverage in the state.
“These bills, while intended to address rising insurance costs, would have the opposite impact and likely harm consumers by reducing competition and increasing costs for Illinois drivers,” said a press release issued by the American Property Casualty Insurance Association, the Illinois Insurance Association, and the National Association of Mutual Insurance Companies. “Insurance rates are first and foremost a function of claims and their costs. Rather than working to help make roadways safer and reduce costs, these bills seek to change the state’s insurance rating law and prohibit the use of factors that are highly predictive of the risk of a future loss.”
The proposed laws would bar insurers from considering nondriving factors that are demonstrably predictive of claims when setting premium rates.
“Prohibiting highly accurate rating factors…disconnects price from the risk of future loss, which necessarily means high-risk drivers will pay less and lower-risk drivers will pay more than they otherwise would pay,” the release says. “Additionally, changing the rating law and factors used will not change the economics or crash statistics that are the primary drivers of the cost of insurance in the state.”
Triple-I agrees with the key concerns raised by the other trade organizations. As we have written previously, such legislation suggests a lack of understanding about risk-based pricing that is not isolated to Illinois legislators – indeed, similar proposals are submitted from time to time at state and federal levels.
What is risk-based pricing?
Simply put, risk-based pricing means offering different prices for the same level of coverage, based on risk factors specific to the insured person or property. If policies were not priced this way – if insurers had to come up with a one-size-fits-all price for auto coverage that didn’t consider vehicle type and use, where and how much the car will be driven, and so forth – lower-risk drivers would subsidize riskier ones. Risk-based pricing allows insurers to offer the lowest possible premiums to policyholders with the most favorable risk factors. Charging higher premiums to insure higher-risk policyholders enables insurers to underwrite a wider range of coverages, thus improving both availability and affordability of insurance.
This simple concept becomes complicated when actuarially sound rating factors intersect with other attributes in ways that can be perceived as unfairly discriminatory. For example, concerns have been raised about the use of credit-based insurance scores, geography, home ownership, and motor vehicle records in setting home and car insurance premium rates. Critics say this can lead to “proxy discrimination,” with people of color in urban neighborhoods sometimes charged more than their suburban neighbors for the same coverage.
The confusion is understandable, given the complex models used to assess and price risk and the socioeconomic dynamics involved. To navigate this complexity, insurers hire teams of actuaries and data scientists to quantify and differentiate among a range of risk variables while avoiding unfair discrimination.
While it may be hard for policyholders to believe factors like age, gender, and credit score have anything to do with their likelihood of filing claims, the charts below demonstrate clear correlations.
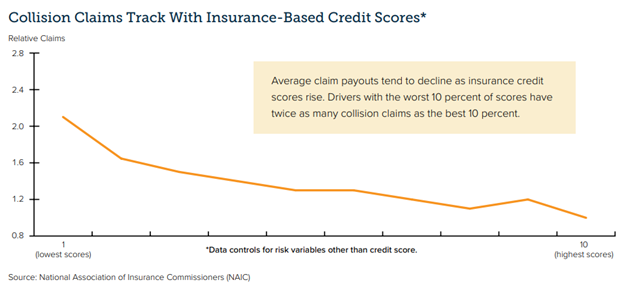
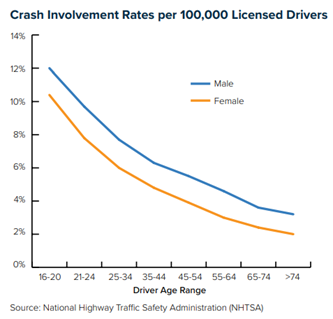
Policyholders have reasonable concerns about rising premium rates. It’s important for them and their legislators to understand that the current high-rate environment has nothing to do with the application of actuarially sound rating factors and everything to do with increasing insurer losses associated with higher frequency and severity of claims. Frequency and claims trends are driven by a wide range of causes – such as riskier driving behavior and legal system abuse – that warrant the attention of policymakers. Legislators would do well to explore ways to reduce risks, contain fraud other forms of legal system abuse, and improve resilience, rather than pursuing “solutions” to restrict pricing that will only make these problem worse.
Learn More
New Triple-I Issues Brief Takes a Deep Dive into Legal System Abuse
Illinois Bill Highlights Need for Education on Risk-Based Pricing of Insurance Coverage
How Proposition 103 Worsens Risk Crisis in California
Louisiana Still Least Affordable State for Personal Auto, Homeowners Insurance
IRC Outlines Florida’s Auto Insurance Affordability Problems
Education Can Overcome Doubts on Credit-Based Insurance Scores, IRC Survey Suggests
Colorado’s Life Insurance Data Rules Offer Glimpse of Future for P&C Writers
It’s Not an “Insurance Crisis” – It’s a Risk Crisis
Indiana Joins March Toward Disclosure of Third-Party Litigation Funding Deals
Litigation Funding Law Found Lacking in Transparency Department
[ad_2]
Source link