[ad_1]

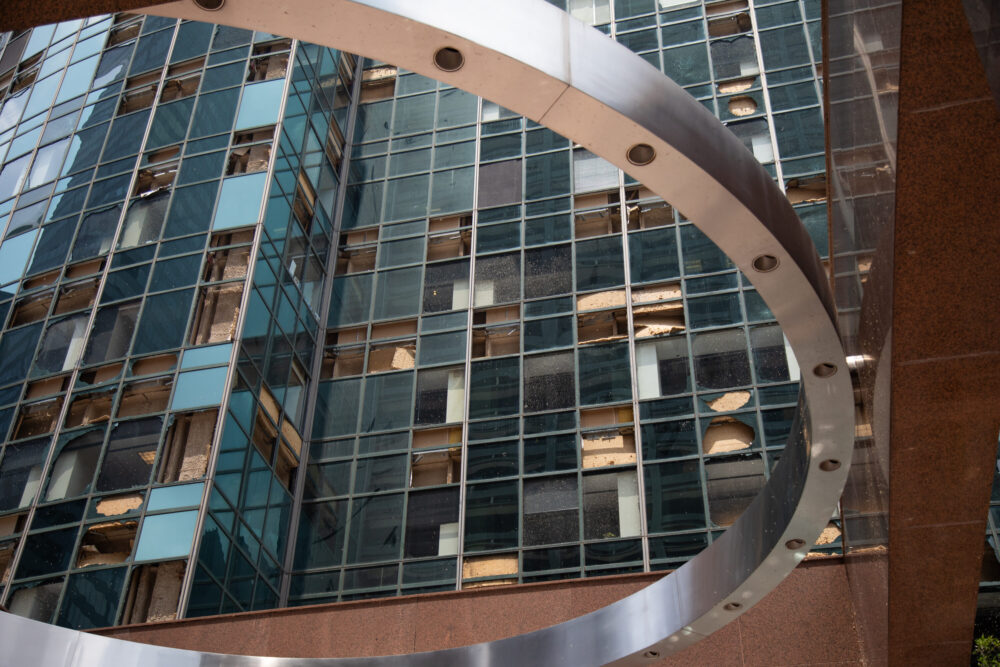
Last week’s earthquake in Lebanon, N.J. – the strongest to hit the state in more than 200 years and which halted activity in New York-area airports and was felt from Washington, D.C., to Maine – highlighted the importance of earthquake preparedness, mitigation, and insurance in areas traditionally not associated with damaging seismic activity.
Earthquake insurance is not covered under a standard homeowners policy. According to A.M. Best, $250 million in direct premiums written for earthquake coverage was in force in Connecticut, New Jersey, and New York in 2023, accounting for less than 5 percent of U.S. earthquake coverage premiums.
Claims from last week’s event are not expected to be excessive.
“Insurers may be anticipating small claims from owners of businesses,” said Janet Ruiz, Triple-I director of strategic communication. “For example, grocery stores, where glass bottles may have fallen from shelves. But the insurance impact is likely to be limited.”
The most significant impact occurred in Newark, N.J., where three multifamily row homes were declared uninhabitable because of potential structural damage, displacing dozens of residents. However, on Saturday morning, the properties were declared structurally safe and residents were allowed to return.
Earthquakes large enough to be felt by a lot of people are relatively uncommon on the East Coast. Since 1950 there have been about 20 quakes with a magnitude above 4.5, according to the United States Geological Survey. That’s compared with over 1,000 on the West Coast.
In 2011, a 5.8 magnitude quake near Mineral, Va., shook East Coast residents over a wide swath from Georgia to Maine and even southeastern Canada. The USGS called it one of the most widely felt quakes in North American history. The quake cost $200 to $300 million in property damages, including to the Washington Monument in D.C., much of it uninsured.
Just as floods can inflict damage in areas not designated by FEMA as “flood zones,” any property where a quake can happen can undergo significant damage. Unlike in earthquake-prone states like California, however, structures typically are not designed or built with seismic events in mind. Homeowners would be well advised to discuss with their insurance professionals whether earthquake coverage is right for them.
Last week’s temblor also should drive awareness of the need for Congress to reauthorize the National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program (NEHRP) – a federal program that helps mitigate earthquake damage to buildings and communities. The NEHRP expired in September 2023. Bipartisan legislation to reauthorize the program was introduced in January 2024.
“I’ve seen what happens when communities aren’t prepared and haven’t mitigated,” said Dr. Lucy Arendt, a professor with St. Norbert College and Chair of the NEHRP Advisory Committee on Earthquake Hazards Reduction, in a March 7 congressional briefing hosted by the National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS). “People are displaced from their homes. Schools are closed. Businesses shutter. There’s a lot of trauma.”
Arendt said investment in knowledge, time, and money prior to a severe disaster is significantly less than the cost to help communities recover from a major threat.
“There is a resilience gap between where we are today and where we should be as a resilient nation,” said Daniel Kaniewski, a former FEMA deputy administrator and member of the NIBS Multi-Hazard Mitigation Council. “I saw firsthand the collapse of infrastructure. These are things you might not see because it’s buried underground. But without water and power, that community cannot recover. Lifeline infrastructure needs to be restored quickly and efficiently.”
Most of the built environment is not designed to withstand earthquakes. Communities with weak building codes, older housing stock, unreinforced masonry buildings, and unmitigated hazards will fare worse than others, Kaniewski said.
“This, combined with the potential severe human toll, means that any U.S. earthquake could have catastrophic consequences that would reverberate well beyond the impact zone,” he added. “Damage to manufacturing facilities, transportation nodes, and communications networks and disrupted supply chains would be among the long list of cascading failures. Massive government spending would be necessary” to repair in the aftermath of such an event.
Learn More:
Triple-I Backgrounder on Earthquake Risk
Triple-I Facts & Statistics: Earthquakes and Tsunamis
Earthquakes: You Can’t Predict Them, But You Can Prepare
California Earthquakes: How Modern Building Codes Are Making Safer, More Resilient Communities
[ad_2]
Source link






 || Flock Finger Lakes
|| Flock Finger Lakes 
